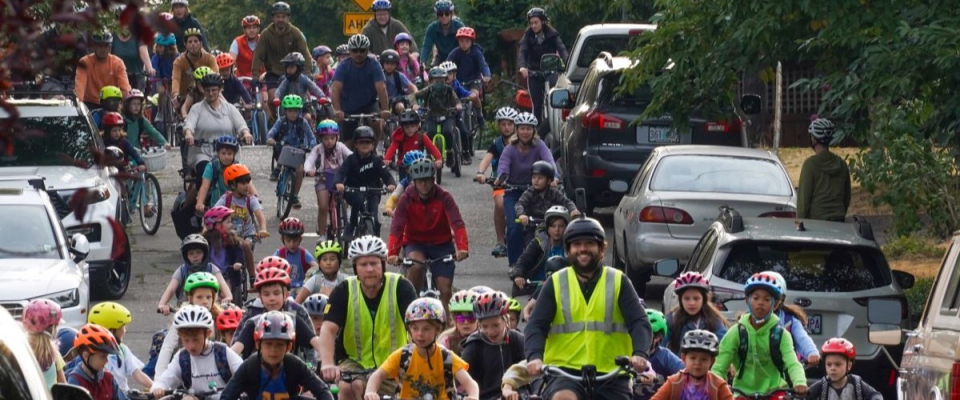
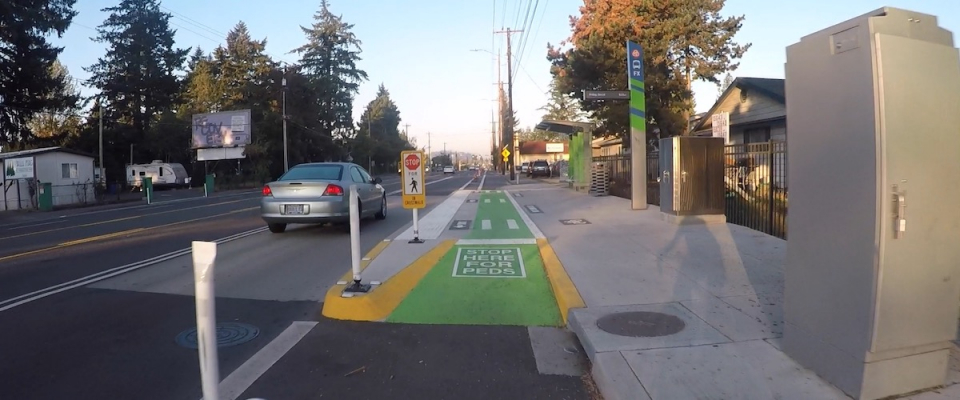
Over the past several years, in a series of research projects, researchers at Portland State University (PSU) have been developing a new approach to estimate active transportation volumes using machine learning.
This emerging method, which can predict how many people will be biking or walking on any given road, trail or segment of a transportation network at any time, offers promising applications for transportation agencies and state departments of transportation (DOTs). These organizations can use accurate bicycle and pedestrian volume information to track changes over time, prioritize projects, plan and design new infrastructure, conduct safety analyses and estimate public health impacts.
"These methods are still evolving, and it's still in the research phase. But I think the time is not far off when we will start using these methods as more mainstream," said Sirisha Kothuri of the Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer Science, the lead researcher on this series of projects.
The method Kothuri and other researchers are developing is referred to as "data fusion" because it involves combining multiple data sources, including traditional permanent and short-term counting methods as well as newer crowdsourced data streams from entities like Strava and Streetlight.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
Traditional permanent and short-term counting methods can directly provide counts, but are limited to certain...
Read more