Navigating an unfamiliar place is uniquely challenging for people with disabilities. People with blindness, deafblindness, visual impairment or low vision, as well as those who use wheelchairs, can travel more independently in urban areas with the aid of effective wayfinding technology. A new report from the National Institute for Transportation and Communities (NITC) explores how to leverage low-cost methods to enable people to more easily move through public, urban indoor and outdoor spaces.
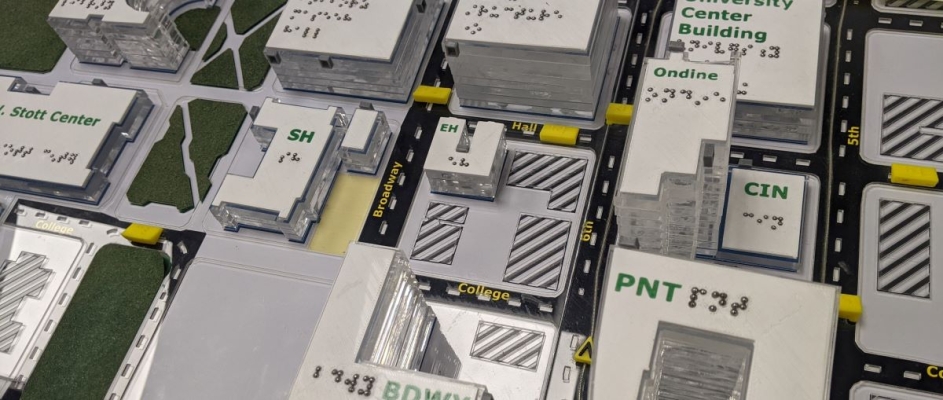
The study, led by Martin Swobodzinski and Amy Parker of Portland State University, used focus groups, two case studies, and an in-person structured wayfinding experience on the PSU campus to find the most helpful ways of getting around. Tactile maps were found to be a very useful resource, with an accessible mobile app also showing promise as an orientation and mobility aid.
The researcher will share more details about this project in a free webinar on December 15: Individual Wayfinding in the Context of Visual Impairment, Blindness, and Deafblindness.
WHY IS THIS RESEARCH IMPORTANT?
Environments and...
Read more